By Alecia Sexton
Layout Manager
Inflammation is defined by the National Institute of Health (NIH) as the body’s natural response to real or perceived harmful substances and injuries. Some important vitamins and minerals that help support the immune system include vitamin C, vitamin B and zinc.
Vitamin C increases the concentration and speed of cells that heal the body, and it decreases inflammation, while vitamin B6 promotes healthy red blood cells that carry oxygen and nutrients through the body. Zinc shortens the duration and strengthens the effectiveness of any and all immune system responses.
Short term inflammation helps deliver blood and nutrients to muscles, bones, and other areas to help them heal after an injury. It also helps form blood clots so that invading organisms cannot enter the general circulatory system and spread throughout the body. These actions make inflammation a healthy and necessary survival process.
On the other hand, chronic, long term inflammation can be critically damaging to the body since it destroys tissues and hinders the function of vital organs. What’s worse is that long term inflammation, as supported by the NIH, can lead to conditions such as diabetes, obesity, digestive diseases, and even cancer.
Due to modern-day lifestyles consisting of stress triggers such as alcohol, environmental pollution, and low-quality food, the number of chronic inflammatory diseases is higher now than it has ever been. Some common causes include mental stress from too many obligations as well as physical stress from lack of sleep and overworking the body. This prevents proper muscle and tissue repair.
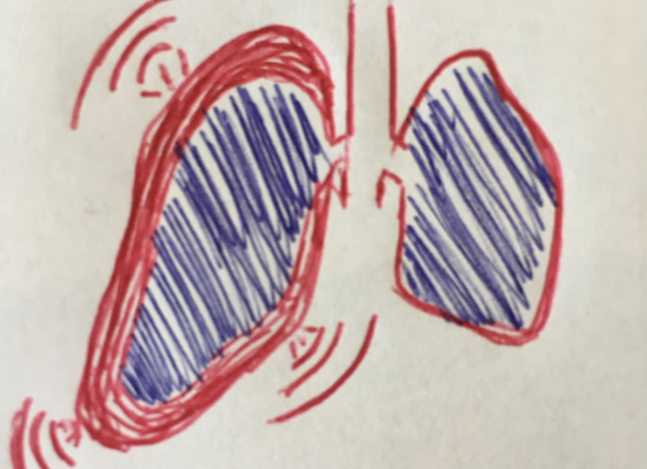
A primary cause of inflammation that we may overlook in our daily lives is smoking. Smoking cigarettes, as well as being exposed to secondhand smoke, leads to not only lung inflammation but inflammation throughout the body. Cigarettes contain toxins such as pesticides, arsenic and lead that are released into the environment. As stated in studies done by the NIH, these substances attach to fat cells and make it harder to lose weight, since the toxins are stored in fat to prevent them from affecting vital tissues such as the brain, heart and lungs.
While it’s impossible to control every pro-inflammatory aspect of our lives, it’s important to spread the word about inflammation so we can all help promote life long health and wellness in our community.
Editor’s Note: The Pioneer is not responsible for giving medical advice. Please refer to a medical professional for serious concerns.




Be First to Comment